Table of Contents
SIMATIC HMI HMI device KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic
SIMATIC HMI
HMI device
KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic,
KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic
Operating Instructions
The following supplement is part of this documentation:
No.
Designation
1
Product Information
08/2008
A5E01075587-01
Drawing number
Edition
A5E02296525-01
08/2008
Preface
______________
Overview
Safety instructions and
______________
general notes
______________
Mounting and connecting
______________
Operating the user interface
Configuring the operating
______________
system
______________
Commissioning a project
______________
Maintenance and care
______________
Technical specifications
______________
Appendix
______________
Abbreviations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
B
Table of Contents

Summary of Contents for Siemens SIMATIC KTP400 Basic
- Page 1 Preface SIMATIC HMI HMI device KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic ______________ Overview Safety instructions and ______________ general notes SIMATIC HMI ______________ Mounting and connecting HMI device ______________ KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, Operating the user interface KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Configuring the operating ______________ system...
- Page 2 Trademarks All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of the Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
-
Page 3: Preface
Preface Purpose of the operating instructions These operating instructions provide information based on the requirements defined by IEC 62079 for documentation. This information relates to the HMI device, its storage, transportation, place of use, installation, use and maintenance. These operating instructions are intended for a variety of target groups. The following table shows the sections of these operating instructions that are of particular importance for the respective target group. - Page 4 Preface Basic knowledge required Knowledge of automation technology and process communication is necessary to understand the operating instructions. An understanding of the use of computers and operating systems is also required. Photos Photographs are sometimes used to illustrate the HMI devices in these operating instructions.
- Page 5 Trademarks Names labeled with a ® symbol are registered trademarks of the Siemens AG. Other names used in this documentation may be trademarks, the use of which by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
- Page 6 Preface Additional information You can find additional information and support for products described in the manual in the following table: Request Contact Representatives and offices http://www.siemens.com/automation/partner Additional technical documentation http://www.automation.siemens.com/simatic/portal/html_76/tec hdoku.htm Training Center Tel: +49 911 895 3200 http://www.sitrain.com Technical Support...
-
Page 7: Table Of Contents
Table of contents Preface ..............................3 Overview..............................11 Product Overview.........................11 Design of the KTP400 Basic HMI device..................12 Design of the KTP600 DP Basic HMI device................13 Design of the KTP600 PN Basic HMI device................14 Design of the KTP1000 DP Basic HMI device................15 Design of the KTP1000 PN Basic HMI device................16 Design of the TP1500 Basic HMI device ..................17 Product package ..........................18... - Page 8 Table of contents Entering data on the KTP600, KTP1000, TP1500 Basic ............47 Configuring the operating system ......................49 Opening the Control Panel......................49 Overview ............................. 50 Changing MPI/DP settings ......................51 Changing the network configuration ................... 52 Changing monitor settings ......................53 Displaying information about the HMI device................
- Page 9 Table of contents Information on insulation tests, protection class and degree of protection........85 Power supply..........................86 Dimension drawings........................87 8.7.1 Dimensional drawing of KTP400 Basic..................87 8.7.2 Dimensional drawing of KTP600 DP Basic..................88 8.7.3 Dimensional drawing of KTP600 PN Basic..................89 8.7.4 Dimensional drawing of KTP1000 DP Basic................90 8.7.5 Dimensional drawing of KTP1000 PN Basic................91 8.7.6...
- Page 10 Table of contents KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01...
-
Page 11: Overview
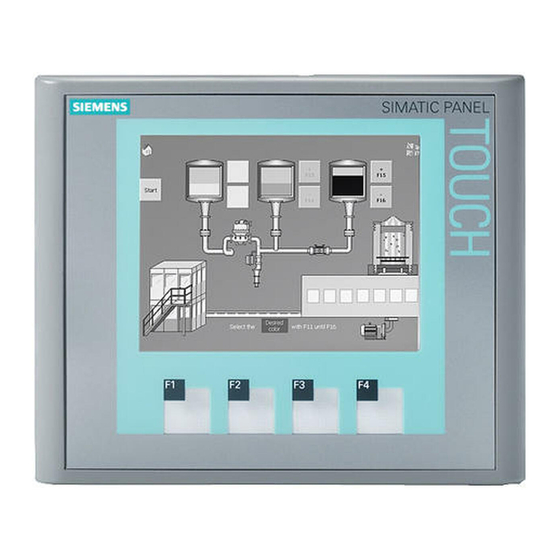
Overview Product Overview Focused on fundamentals - the new basic panels Visualization is part of the standard repertoire for most machines these days. The cost factor plays a crucial role in this case, especially for small machines and simple applications. HMI devices with basic functions are often fully sufficient for simple applications. -
Page 12: Design Of The Ktp400 Basic Hmi Device
Overview 1.2 Design of the KTP400 Basic HMI device Design of the KTP400 Basic HMI device ① Recesses for mounting clamps ⑥ Connection for functional ground ② Display / touch screen ⑦ PROFINET interface ③ Mounting seal ⑧ Power supply connector ④... -
Page 13: Design Of The Ktp600 Dp Basic Hmi Device
Overview 1.3 Design of the KTP600 DP Basic HMI device Design of the KTP600 DP Basic HMI device ① Display / touch screen ⑦ Power supply connector ② Recesses for mounting clamps ⑧ Rating plate ③ Mounting seal ⑨ Interface name ④... -
Page 14: Design Of The Ktp600 Pn Basic Hmi Device
Overview 1.4 Design of the KTP600 PN Basic HMI device Design of the KTP600 PN Basic HMI device ① Display / touch screen ⑦ Power supply connector ② Recesses for mounting clamps ⑧ Rating plate ③ Mounting seal ⑨ Interface name ④... -
Page 15: Design Of The Ktp1000 Dp Basic Hmi Device
Overview 1.5 Design of the KTP1000 DP Basic HMI device Design of the KTP1000 DP Basic HMI device ① Display / touch screen ⑦ Rating plate ② Recesses for mounting clamps ⑧ DIP switch ③ Mounting seal ⑨ Interface name ④... -
Page 16: Design Of The Ktp1000 Pn Basic Hmi Device
Overview 1.6 Design of the KTP1000 PN Basic HMI device Design of the KTP1000 PN Basic HMI device ① Display / touch screen ⑦ Rating plate ② Recesses for mounting clamps ⑧ DIP switch ③ Mounting seal ⑨ Interface name ④... -
Page 17: Design Of The Tp1500 Basic Hmi Device
Overview 1.7 Design of the TP1500 Basic HMI device Design of the TP1500 Basic HMI device ① Display / touch screen ⑤ Power supply connector ② Recesses for mounting clamps ⑥ Rating plate ③ Mounting seal ⑦ Interface name ④ PROFINET interface ⑧... -
Page 18: Product Package
Overview 1.8 Product package Product package Product package The following components are included in the product package of the HMI device. Name Figure Quantity HMI device Installation instructions Mounting seal Clamps with stud bolts KTP400 Basic KTP600 Basic KTP1000 Basic TP1500 Basic Mains terminal KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic... -
Page 19: Accessories
1.9 Accessories Accessories The following accessories are available for the HMI devices in the Internet at http://mall.automation.siemens.com. RS 422 to RS 232 converter The converter is required to connect a SIMATIC S5 PLC and PLCs from other manufacturers. Connect the RS 422 to RS 232 converter to the RS 422 / RS 485 interface. -
Page 20: Commissioning The Hmi Device
Overview 1.10 Commissioning the HMI device PROFIBUS bus connector We recommend using straight PROFIBUS bus connectors. The connectors are not included in the product package of the HMI device. The connectors are available under order number 6GK1 500-0FC10. Clamping frame A clamping frame is available for the KTP1000 HMI under order number 6AV6 671-8XS00-0AX0. -
Page 21: Safety Instructions And General Notes
Safety instructions and general notes Safety instructions Working on the control cabinet WARNING Open equipment The HMI device is open equipment. That is, the HMI device may only be installed in cubicles or cabinets which provide front panel access for operating the device. The cubicle or cabinet in which the HMI device is installed may only be accessed with a key or tool and only by trained, authorized personnel. -
Page 22: Notes About Usage
Safety instructions and general notes 2.2 Notes about usage Notes about usage Industrial applications The HMI device is designed for industrial applications. It conforms to the following standards: ● Requirements of the emission standard for industrial environments, EN 61000-6-4: 2007 ●... -
Page 23: Mounting And Connecting
Damaged parts Do not install parts damaged during shipment. In the case of damaged parts, contact your Siemens representative. The package content is described in section Product package (Page 18). Keep the supplied documentation in a safe place. The documentation belongs to the HMI device and is required for subsequent commissioning. -
Page 24: Selecting A Mounting Position
Mounting and connecting 3.1 Preparations 3.1.3 Selecting a mounting position Select one of the approved mounting positions for your HMI device. The approved mounting positions are described in the following sections. Horizontal mounting positions All Basic HMI devices are suitable for horizontal mounting positions. -
Page 25: Checking Clearances
Mounting and connecting 3.1 Preparations 3.1.4 Checking clearances The following clearances are required around the HMI device to ensure sufficient self-ventilation: Required clearance around the HMI devices. All Basic KTP400 Panels KTP600 All dimensions in mm 3.1.5 Making the mounting cut-out NOTICE Stability of the mounting cut-out The material in the area of the mounting cut-out must provide sufficient strength to... - Page 26 Mounting and connecting 3.1 Preparations Mounting compatibility The mounting cut-outs of the Basic panels are compatible with the mounting cut-outs of the following SIMATIC HMI devices: Mounting cut-out for the Basic Compatible to the mounting cut-outs of the HMI device Panel KTP400 TP 177B 4"...
-
Page 27: Labeling The Function Keys
Mounting and connecting 3.1 Preparations 3.1.6 Labeling the function keys Note Do not write on the keyboard to label the function keys. Any printable and writable foil can be used as labeling strips. The permitted thickness of the labeling strip is 0.15 mm. Paper labeling strips are inappropriate. 1. -
Page 28: Mounting The Hmi Device
Mounting and connecting 3.2 Mounting the HMI device Mounting the HMI device Required tools and accessories Before beginning mounting, have the following tools and accessories at hand: Slotted screwdriver, size 2 Mounting clamps KTP400 Basic: 5 • • KTP600 Basic: 8 •... - Page 29 Mounting and connecting 3.2 Mounting the HMI device Securing the HMI device 1. Insert the first clamp at the first position of the recesses on the back of the HMI device. Set the clamp positions for your HMI device to match those of the figures in the following table row.
-
Page 30: Connecting The Hmi Device
Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device Connecting the HMI device 3.3.1 Connection sequence Required tools and accessories Before beginning the connection of the HMI device, have the following tools and accessories at hand: Screwdriver: Slotted screwdriver, size 2 •... -
Page 31: Connecting The Equipotential Bonding Circuit
Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device 3.3.2 Connecting the equipotential bonding circuit Differences in electrical potential Differences in electrical potential can develop between spatially separated plant components. Such electrical potential differences can lead to high equalizing currents over the data cables and therefore to the destruction of their interfaces. - Page 32 Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device Procedure 1. Interconnect functional ground of the HMI device with an grounding cable, cross-section 4 mm 2. Connect the grounding cable of the HMI device to the equipotential bonding rail. KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01...
-
Page 33: Connecting The Power Supply
Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device 3.3.3 Connecting the power supply Stripping the cable Use power supply cables with a maximum cross-section of 1.5 mm 1. Strip the ends of both power supply cables to a length of 6 mm. 2. -
Page 34: Connecting A Programming Device
Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device 3.3.4 Connecting a programming device A programming device provides the following options: ● Transferring projects. ● Transferring device images. Connecting a programming device to a Basic Panel DP Note A programming device cannot be used to reset the HMI device to factory settings. 1. -
Page 35: Connecting The Configuration Pc
Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device 3.3.5 Connecting the configuration PC A configuration PC provides the following options: ● Transferring projects. ● Transferring device images. ● Resetting HMI device to factory settings. Connecting a configuration PC to a Basic Panel DP 1. - Page 36 Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device Configuring the PC/PPI cable Configure the transmission speed using the DIP switches of the PC/PPI cable if using the PC/PPI cable to interconnect the HMI device with the configuration PC. Note Set a lower bit rate if the connection is lost during the operating system update. If you use a higher bit rate, you must use the PC/PPI cable release 3 or higher.
- Page 37 Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device Connecting a configuration PC to a Basic Panel PN CAUTION Data network security for communication via Ethernet End users are themselves responsible for ensuring security of their data network in Ethernet-based communication, such as PROFINET IO, HTTP, Sm@rtAccess, Sm@rtService and OPC, since operation of the device cannot be guaranteed if the device is subject to targeted attacks resulting in overload, for example.
-
Page 38: Connecting The Plc
Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device 3.3.6 Connecting the PLC Connect the HMI device to the PLC if it contains an operating system and an executable project. Connecting a PLC to a Basic Panel DP You can interconnect Basic Panels DP via RS 422/485 port with the following SIMATIC PLCs: SIMATIC S7-200... - Page 39 Mounting and connecting 3.3 Connecting the HMI device The following table shows the DIP switch settings. The send and receive direction is toggled internally using the RTS signal. Communication Switch setting Meaning DP/MPI/PPI No RTS signal on connector, for data exchange between the SIMATIC PLC and the HMI device (factory state) RTS signal on pin 4, same as PLC,...
-
Page 40: Switching On And Testing The Hmi Device
Mounting and connecting 3.4 Switching on and testing the HMI device Switching on and testing the HMI device Switching on the HMI device. Switching on the power supply. The screen lights up after power is switched on. A progress bar is displayed during startup. If the HMI device fails to start, you have probably crossed the wires on the mains terminal. -
Page 41: Operating The User Interface
Operating the user interface Overview All Basic HMI devices feature a touch screen. Certain Basic HMI devices feature function keys. Use the touch screen and function keys to operate the Control Panel or the project running on your HMI device. DANGER Incorrect operation A project can contain certain operations that require in-depth knowledge about the specific... - Page 42 Operating the user interface 4.1 Overview Examples of operator controls: ● Buttons Buttons can assume the following states: "Untouched" "Touched" ● Invisible buttons The focus of invisible buttons is by default not indicated following selection. No optical operation feedback is provided in this case. The configuration engineer may, however, configure invisible buttons so that their outline appears as lines when touched.
-
Page 43: General Functions Of The Screen Keyboard
Operating the user interface 4.2 General functions of the screen keyboard General functions of the screen keyboard The following keys are available on the screen keyboard of all Basic HMI devices: Cursor left Cursor right Delete character Cancel input Confirm input Display infotext. -
Page 44: Entering Data On The Ktp400 Basic
Operating the user interface 4.3 Entering data on the KTP400 Basic Entering data on the KTP400 Basic Due to the small display, the screen keyboard and the input concept of the KTP400 Basic differs compared to other Basic HMI devices. The screen keyboard appears on the HMI device touch screen when you touch an operator control that requires input. - Page 45 Operating the user interface 4.3 Entering data on the KTP400 Basic Note Job mailbox has no effect PLC job 51 "Select screen" has no effect while the screen keyboard is open. Key assignment The alphanumerical keyboard layout is monolingual. A language change within the project does not have any effect on the layout of the alphanumerical screen keyboard.
-
Page 46
Operating the user interface 4.3 Entering data on the KTP400 Basic Entering numerical values 1. Touch the desired operator control on the screen. The numerical screen keyboard opens. 2. Enter the value. Depending on the settings, the HMI device outputs an audible signal. You can change the view of the screen keyboard for entering numbers with hexadecimal notation using the
... -
Page 47: Entering Data On The Ktp600, Ktp1000, Tp1500 Basic
Operating the user interface 4.4 Entering data on the KTP600, KTP1000, TP1500 Basic Entering data on the KTP600, KTP1000, TP1500 Basic Alphanumerical screen keyboard The screen keyboard appears on the HMI device touch screen when you touch an operator control that requires input. Note Job mailbox has no effect PLC job 51 "Select screen"... - Page 48 Operating the user interface 4.4 Entering data on the KTP600, KTP1000, TP1500 Basic Entering numerical values 1. Touch the desired operator control on the screen. The numerical screen keyboard opens. 2. Enter the value. Depending on the settings, the HMI device outputs an audible signal.
-
Page 49: Configuring The Operating System
Configuring the operating system Opening the Control Panel Open the Control Panel by pressing the "Control Panel" button of the Loader. Configure your HMI device in the Control Panel. You can make the following settings: Communication settings • • Settings for operation Password protection •... -
Page 50: Overview
Configuring the operating system 5.2 Overview Overview The following table shows the functions available in the Control Panel for configuring your HMI device. Symbol Function Changing MPI/DP settings (Page 51) Changing the network configuration (Page 52) Changing monitor settings (Page 53) Displaying information about the HMI device (Page 54) Calibrating the touch screen (Page 55) Displaying licensing information for the HMI device (Page 56) -
Page 51: Changing Mpi/Dp Settings
Configuring the operating system 5.3 Changing MPI/DP settings Changing MPI/DP settings Note The settings for MPI or PROFIBUS DP communication are defined in the HMI device project. Edit the transfer settings only in the following situations: • Initial transfer of a project. •... -
Page 52: Changing The Network Configuration
Configuring the operating system 5.4 Changing the network configuration Changing the network configuration NOTICE Communication errors caused by IP address conflicts Communication errors can occur if several devices in a network share the same IP address. Assign each HMI device an IP address that is unique within the network. 1. -
Page 53: Changing Monitor Settings
Configuring the operating system 5.5 Changing monitor settings Changing monitor settings NOTICE Orientation of the screen for KTP400 Basic and KTP600 Basic The screen orientation is defined by the configuration engineer in the course of project creation. The appropriate screen orientation is set automatically when you transfer the project to the HMI device. -
Page 54: Displaying Information About The Hmi Device
Configuring the operating system 5.6 Displaying information about the HMI device Displaying information about the HMI device 1. Press the "OP" button to open the "OP Properties" dialog. 2. Change to the "Device" tab. The "License" tab is used to display specific information on the HMI device. -
Page 55: Calibrating The Touch Screen
Configuring the operating system 5.7 Calibrating the touch screen Calibrating the touch screen 1. Press the "OP" button to open the "OP Properties" dialog. 2. Change to the "Touch" tab. 3. Press the "Recalibrate" button to open the calibration screen. 4. -
Page 56: Displaying Licensing Information For The Hmi Device
Configuring the operating system 5.8 Displaying licensing information for the HMI device Displaying licensing information for the HMI device 1. Use the "OP" button to open the "OP Properties" dialog. 2. Open the "License" tab. The "License" tab is used to display the licensing information for the software of the HMI device. -
Page 57: Enabling A Data Channel
Configuring the operating system 5.9 Enabling a data channel Enabling a data channel You must enable at least one data channel to transfer a project to the HMI device. Note After having completed the project transfer, you can protect the HMI device against unintentional overwriting of project data and of the HMI device image by locking all data channels. - Page 58 Configuring the operating system 5.9 Enabling a data channel Enabling a data channel - Basic Panels PN 1. Press the "Transfer" button to open the "Transfer Settings" dialog. 2. Select the "Enable Channel" check box in the "Channel 1" field. Press the "Advanced"...
-
Page 59: Changing Password Settings
Configuring the operating system 5.10 Changing password settings 5.10 Changing password settings Password protection prevents unauthorized access to the Control Panel. NOTICE The password cannot contain spaces or special characters * ? . % / \ ' ". If the password is no longer available for the Control Panel, you first have to update the operating system before you can make any changes in the Control Panel. -
Page 60: Setting The Screen Saver
Configuring the operating system 5.11 Setting the Screen Saver 5.11 Setting the Screen Saver NOTICE Burn-in effect The screen contents may leave a faint version (ghost) of the image in the background if they appear for too long. The "ghost" will disappear automatically after some time. The longer the same content is displayed on the screen, the longer it will take for the burn-in effect to disappear. -
Page 61: Commissioning A Project
Commissioning a project Overview Configuration phase A project – the process image of the working process – is produced during configuration to visualize automated working processes. The process displays for the project contain displays for values and messages which provide information about process statuses. The process control phase follows the configuration phase. -
Page 62: Operating Modes
Commissioning a project 6.2 Operating modes Operating modes Operating modes The HMI device may be in the following operating modes: ● Offline ● Online ● Transfer "Offline mode" and "Online mode" can be set on both the configuring PC and the HMI device. -
Page 63: Data Transmission Options
Commissioning a project 6.3 Data transmission options Data transmission options Overview The following table shows the options for data transfer between the HMI device and configuration PC. Type Data channel Basic Panels DP Basic Panels PN Backup/restore, Serial Operating system update MPI/PROFIBUS DP Project transfers PROFINET... -
Page 64: Starting Automatic Transfer
Commissioning a project 6.4 Transfer Procedure Proceed as follows: 1. On the configuration PC, select the "Transfer settings" command from the "Project > Transfer" menu in WinCC flexible. The "Select devices for transfer" dialog opens. 2. Select the HMI device in the left area of the dialog. 3. - Page 65 Commissioning a project 6.4 Transfer NOTICE If automatic transfer is activated on the HMI device and a transfer is initiated on the configuration PC, the project currently running is automatically stopped. The HMI device then automatically switches to "Transfer" mode. After the commissioning phase, deactivate the automatic transfer so that the HMI device cannot be inadvertently switched to transfer mode.
-
Page 66: Testing A Project
Commissioning a project 6.4 Transfer 6.4.4 Testing a project Introduction There are two options to test a project: ● Test the project on the configuring PC You can test a project at a configuring PC, using a simulator. For detailed information, refer to the "WinCC flexible"... - Page 67 Commissioning a project 6.4 Transfer Procedure In "Offline" mode, you can test individual project functions on the HMI device without them being affected by the PLC. PLC tags, therefore, are not updated. Test the operating elements and visualization of the project as far as possible without connecting to the PLC.
-
Page 68: Backup And Restore
Commissioning a project 6.5 Backup and restore Backup and restore 6.5.1 Overview Backup and restore You can back up and restore the following data found in the internal flash memory of the HMI device with a PC: ● Project and HMI device image ●... -
Page 69: Backup And Restore Using Wincc Flexible
Commissioning a project 6.5 Backup and restore 6.5.2 Backup and restore using WinCC flexible Requirement ● No project is open on the configuration PC in WinCC flexible. ● The HMI device is connected to this configuration PC. ● The data channel is programmed on the HMI device. Procedure –... - Page 70 Commissioning a project 6.5 Backup and restore Procedure – restoring Proceed as follows: 1. On the configuration PC, select the "Communication settings" command in the menu "Project > Transfer" in WinCC flexible. The "Communication settings" dialog box opens. 2. Select the type of HMI device. 3.
-
Page 71: Backup And Restore Using Prosave
Commissioning a project 6.5 Backup and restore 6.5.3 Backup and restore using ProSave Requirements ● The HMI device is connected to a PC on which ProSave is installed. ● The data channel is parameterized on the HMI device. Procedure – backup Proceed as follows: 1. - Page 72 Commissioning a project 6.5 Backup and restore Procedure – restore Proceed as follows: 1. Go to the Windows Start menu and start ProSave on the PC. 2. Select the HMI device type in the "General" tab. 3. Select the type of interconnection for the HMI device and the PC. 4.
-
Page 73: Updating The Operating System
Commissioning a project 6.6 Updating the operating system Updating the operating system 6.6.1 Overview Updating the operating system A compatibility conflict may occur when transferring a project to the HMI device. This is caused by different versions of the configuration software used and the HMI device image available on the HMI device. -
Page 74: Resetting Factory Settings
Commissioning a project 6.6 Updating the operating system 6.6.2 Resetting factory settings In ProSave or WinCC flexible, you can perform an operating system update with or without reset to factory settings. ● Updating the operating system without reset to factory settings First, switch into "Transfer"... -
Page 75: Updating The Operating System Using Wincc Flexible
Commissioning a project 6.6 Updating the operating system 6.6.3 Updating the Operating System using WinCC flexible Requirements ● The HMI device is connected to a configuration PC. ● No project is open in WinCC flexible. ● When updating the operating system without reset to factory setting only: The data channel is configured on the HMI device. -
Page 76: Updating The Operating System Using Prosave
Commissioning a project 6.6 Updating the operating system 6.6.4 Updating the Operating System using ProSave Requirements ● The HMI device is connected to a PC on which ProSave is installed. ● When updating the operating system without reset to factory settings only: The data channel is configured on the HMI device. -
Page 77: Maintenance And Care
Maintenance and care Maintenance and care Introduction The HMI device is designed for maintenance-free operation. The touch screen and keyboard membrane should nevertheless be cleaned regularly. Requirements Use a cleaning cloth dampened with a cleaning agent to clean the equipment. Only use water with a little liquid soap or a screen cleaning foam. -
Page 78: Recycling
Maintenance and care 7.2 Recycling Recycling Recycling and disposal The HMI devices described in these operating instructions can be recycled due to the low levels of pollutants. Contact a certified disposal service company for environmentally sound recycling and disposal of your old devices. KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 79: Technical Specifications
● Specific absorption rate to EN 50392 EC Declaration of Conformity The EC Declarations of Conformity are available to the relevant authorities at the following address: Siemens AG Industry Sector I IA AS RD ST PLC PO Box 1963 D-92209 Amberg... -
Page 80: Electromagnetic Compatibility
Technical specifications 8.2 Electromagnetic compatibility UL approval Underwriters Laboratories Inc., to ● UL 508 (Industrial Control Equipment) ● CSA C22.2 No. 142 (Process Control Equipment) IEC 61131 The HMI device fulfills requirements and criteria to IEC 61131-2, Programmable Logic Controllers, Part 2: Operating resource requirements and tests. Electromagnetic compatibility Introduction The HMI device fulfills, among other things, the requirements of the EMC laws pertaining to... - Page 81 Technical specifications 8.2 Electromagnetic compatibility Pulse-shaped disturbance The following table shows the electromagnetic compatibility of modules with regard to pulse- shaped interference. The precondition for electromagnetic compatibility is that the HMI device meets the specifications and guidelines for electrical installation. Pulse-shaped disturbance Tested with Degree of...
-
Page 82: Transport And Storage Conditions
Technical specifications 8.3 Transport and storage conditions Transport and storage conditions Mechanical and climatic conditions for transportation and storage The transport and storage conditions of this HMI device exceed requirements in accordance with IEC 61131-2. The following specifications apply to the transport and storage of an HMI device in its original packaging. -
Page 83: Conditions Of Use
Technical specifications 8.4 Conditions of use Conditions of use Mechanical and climatic conditions of use The HMI device is designed for use in a location protected from the effects of the weather. The conditions of use are compliant with requirements to DIN IEC 60721-3-3: ●... - Page 84 Technical specifications 8.4 Conditions of use Testing mechanical ambient conditions The following table provides information on the type and scope of tests for mechanical ambient conditions. Tested for Test standard Comments Vibrations Vibration test in accordance Type of vibration: with IEC 60068, part 2–6 Transitional rate of the frequency: (sinusoidal) 1 octave/minute.
-
Page 85: Information On Insulation Tests, Protection Class And Degree Of Protection
Technical specifications 8.5 Information on insulation tests, protection class and degree of protection Information on insulation tests, protection class and degree of protection Test voltages Insulation strength is demonstrated in the type test with the following test voltages in accordance with IEC 61131-2: Circuits with a nominal voltage of U to other Test voltage... -
Page 86: Power Supply
Technical specifications 8.6 Power supply Power supply CAUTION Safe electrical isolation Use only 24 VDC power supply units with safe electrical isolation in accordance with IEC 60364-4-41 or HD 384.04.41 (VDE 0100, Part 410), e.g. to PELV standard. The supply voltage must be within the specified voltage range. Otherwise, malfunction at the HMI device cannot be ruled out. -
Page 87: Dimension Drawings
Technical specifications 8.7 Dimension drawings Dimension drawings 8.7.1 Dimensional drawing of KTP400 Basic KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 88: Dimensional Drawing Of Ktp600 Dp Basic
Technical specifications 8.7 Dimension drawings 8.7.2 Dimensional drawing of KTP600 DP Basic KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 89: Dimensional Drawing Of Ktp600 Pn Basic
Technical specifications 8.7 Dimension drawings 8.7.3 Dimensional drawing of KTP600 PN Basic KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 90: Dimensional Drawing Of Ktp1000 Dp Basic
Technical specifications 8.7 Dimension drawings 8.7.4 Dimensional drawing of KTP1000 DP Basic KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 91: Dimensional Drawing Of Ktp1000 Pn Basic
Technical specifications 8.7 Dimension drawings 8.7.5 Dimensional drawing of KTP1000 PN Basic KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 92: Dimensional Drawing Of Tp1500 Basic
Technical specifications 8.7 Dimension drawings 8.7.6 Dimensional drawing of TP1500 Basic KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... -
Page 93: Specifications
Technical specifications 8.8 Specifications Specifications 8.8.1 Specifications of the KTP400 Basic and KTP600 Basic Weight KTP400 Basic KTP600 Basic KTP600 Basic Color KTP600 Basic Color Mono PN Mono PN Weight without packaging Approx. 320 g Approx. 1070 g Display KTP400 Basic KTP600 Basic KTP600 Basic KTP600 Basic... - Page 94 Technical specifications 8.8 Specifications Interfaces KTP400 Basic KTP600 Basic KTP600 Basic KTP600 Basic Mono PN Mono PN Color DP Color PN 1 x RS 422/RS 485 Max. 12 Mbps 1 x Ethernet RJ45 10/100 Mbps RJ45 10/100 Mbps RJ45 10/100 Mbps Supply voltage KTP400 Basic KTP600 Basic...
-
Page 95: Specifications Of The Ktp1000 Basic And Tp1500 Basic
Technical specifications 8.8 Specifications 8.8.2 Specifications of the KTP1000 Basic and TP1500 Basic HMI device KTP1000 Basic Color DP KTP1000 Basic Color PN TP1500 Basic Color PN Weight without packaging Approx. 2.65 kg Approx. 4.2 kg Display KTP1000 Basic Color DP KTP1000 Basic Color PN TP1500 Basic Color PN Type... - Page 96 Technical specifications 8.8 Specifications Supply voltage KTP1000 Basic Color DP KTP1000 Basic Color PN TP1500 Basic Color PN Rated voltage +24 VDC Range, permissible 19.2 to 28.8 V (–20%, +20%) Transients, maximum permissible 35 V (500 ms) Time between two transients, 50 s minimum Current consumption...
-
Page 97: Functional Scope With Wincc Flexible
Technical specifications 8.9 Functional Scope with WinCC flexible Functional Scope with WinCC flexible The following tables show the objects that can be integrated in a project for a Basic Panel. Alarms Object Specification Basic Panels Alarms Number of discrete alarms Number of analog alarms Length of the alarm text 80 characters... - Page 98 Technical specifications 8.9 Functional Scope with WinCC flexible Recipes The specified values are maximum values and should not be used additive. Object Specification Basic Panels Recipes Quantity Elements per recipe Data records per recipe Safety Object Specification Basic Panels Safety Number of user groups Number of users Number of authorizations...
-
Page 99: Appendix
Appendix ESD guideline Definition of ESD All electronic modules are equipped with large-scale integrated ICs or components. Due to their design, these electronic elements are highly sensitive to overvoltage, and thus to any electrostatic discharge. These electronic components are therefore specially identified as ESDs. - Page 100 Appendix A.1 ESD guideline Electrostatic charging CAUTION Electrostatic charging ESDs may be destroyed by voltages far below the level perceived by human beings. Voltages of this kind develop when a component or an assembly is touched by a person who is not grounded against static electricity. Usually, it is unlikely that damage to an ESD as a result of overvoltage is detected immediately but may become apparent only after a longer period of operation.
-
Page 101: System Events
"Error code:" System events in the Internet You can find a list of system events for your HMI device in the Internet at http://support.automation.siemens.com. KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01... - Page 102 Appendix A.2 System events KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01...
-
Page 103: Abbreviations
Abbreviations Abbreviations ANSI American National Standards Institution Central Processing Unit Comma Separated Values Clear To Send Direct Current Data Carrier Detect DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Dual-in-Line (electronic chip housing design) Domain Name System Distributed I/O Data Source Name Data Set Ready Data Terminal Ready Input and Output Components and modules endangered by electrostatic discharge... - Page 104 Abbreviations B.1 Abbreviations RJ45 Registered Jack Type 45 Request to send Receive Data SD Card Security Digital Card SELV Safety Extra Low Voltage Service Pack Programmable Logic Controller Super Twisted Nematic Sub-D Subminiature D (plug) Tabulator TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol Thin Film Transistor Teletype Transmit Data...
-
Page 105: Glossary
Glossary "Transfer" mode HMI device operating mode for transferring an executable project from the configuration PC to an HMI device. Acknowledge Acknowledgment of an alarm confirms that it has been noted. Alarm, acknowledgment Acknowledgment of an alarm confirms that it has been noted. Alarm, activated Moment at which an alarm is triggered by the PLC or HMI device. - Page 106 Glossary Configuration software The configuration software is used to create projects for process visualization. WinCC flexible is such a configuration software, for example. Display duration Defines whether a system alarm is displayed on the HMI device and the duration of the display.
- Page 107 Glossary HMI device image The HMI device image is a file that can be transferred from the configuration PC to the HMI device. The HMI device image contains the operating system of the HMI device , including the elements of the Runtime software required for the executable project file. I/O field Enables the input or output of values on the HMI device and their transfer to the PLC.
- Page 108 Glossary Project A project is the result of a configuration using an engineering software. The project usually contains several screens with embedded system-specific objects, basic settings and alarms. A project configured in WinCC flexible is saved to a project file with the extension *.hmi. There is a difference between an offline project on a configuration PC and an online executable project on an HMI device.
- Page 109 Glossary Screen object Refers to objects such as rectangles, I/O fields, or alarm views which are configured for visualization or operation of the plant. STEP 7 STEP 7 is the programming software for SIMATIC S7, SIMATIC C7 and SIMATIC WinAC PLCs.
- Page 110 Glossary KTP400 Basic, KTP600 Basic, KTP1000 Basic, TP1500 Basic Operating Instructions, 08/2008, A5E01075587-01...
-
Page 111: Index
Index Configuring PC, 61 Connecting Configuration PC, 35 Equipotential bonding, 31 Accessories, 19 PLC, 38 Ambient conditions Power supply, 33 Climatic, 84 Programming device, 34 Mechanical, 83 Control cabinet Test, 84 Working on, 21 Application Control Panel In residential areas, 22 Opening, 49 Industrial, 22 Overview, 50... - Page 112 Index Electrostatic, 100 Installation as intended, 21 Precautions, 101 Insulation test, 85 EMC directive, 79 Interfaces Emission, 22, 81 KTP1000, TP1500 Basic, 95 Enabling a data channel, 50 KTP400, KTP600 Basic, 94 Equipotential bonding Internet Cable, 31 Documentation, 6 Connecting, 31 Service, 6 Requirements, 31 Wiring diagram, 32...
- Page 113 Index Touch, 50 Recommissioning, 61 Operating instructions Recycling, 78 Purpose of, 3 Registered trademarks, 5 Scope, 3 Regulations for the prevention of accidents, 21 Operating mode, 62 Representatives, 6 Changing, 62 Restore, 63, 72 Offline, 62 With ProSave, 72 Online, 62 Restoring, 68, 70 Transfer, 62 With WinCC flexible, 70...
- Page 114 Index Display, 93, 95 Project, 61 Input device, 93, 95 Transport conditions, 82 Interfaces, 94, 95 Memory, 93, 95 Supply voltage, 94, 96 Storage conditions, 82 UL approval, 80 Stripping, 33 Update Supply voltage Using ProSave, 76 KTP1000, TP1500 Basic, 96 Using WinCC flexible, 75 KTP400, KTP600 Basic, 94 Updating...
- Page 115 à elle que vous devez vous reporter. Remarque Le pupitre opérateur est uniquement compatible avec les automates suivants dans la première version : ● SIMATIC S7-200 ● SIMATIC S7-300/400 Le pupitre opérateur n'est pas compatible avec des automates d'autres constructeurs. © Siemens Ⓟ2008 A5E02296525-01, 08/2008...
- Page 116 适用性 本产品信息适用于 KTP1000 Basic DP 操作设备,订单号 6AV6647-0AE11-3AX0。 本产品信息包含重要提示。 这些提示对操作设备的操作说明作了必要的补充,比操作说明、发布声明及在线帮助里的信息更 重要。 说明 在第一个阶段的供货中,该操作设备仅兼容下列控制器: ● SIMATIC S7-200 ● SIMATIC S7-300/400 该操作设备不与其他制造商生产的控制器兼容。 Siemens AG Siemens AG Industry Sector Industry Sector Postfach 48 48 Postfach 48 48 90026 NÜRNBERG 90026 NÜRNBERG KTP1000 Basic DP...