Table of Contents
Crosscutting
Repetitive Crosscutting
Repetitive crosscutting is the repeated and
continuous cutting of many pieces of lumber
to the same length. Carriage and length stops
can help make this type of crosscutting more
efficient.
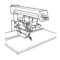
A carriage
stop defines the distance needed
to pull the blade through to complete each
cut. This will prevent pulling the blade
through more than the recommended
dis-
tance.
To make a carriage stop use lx2 lumber:.
i) cut two pieces, each 2" long
ii) clamp a piece on each side of radial
arm, so blade carriage stops at distance
needed to complete cut
iii) check that clamps do not interfere
with hand grip on saw handle.
A length stop defines the cut length and
ensures that all pieces will be cut to the same
size. Clamp a piece of lx2 lumber on the
fence to define the cut length. Use a length
stop only on the end of the workpi_ce
which is held down.
Crosscutting
Hints
1. To extend life of table top, buy auxiliary
table cover (see Accessories)
or make one
out of 1/4" plywood or fiberboard.
Clamp or
nail to original table top, section by section.
If you use nails, nail in the four comers to
make sure blade will not contact nails.
2. Make several fences, so each will have
only a few kerfs (See Cutting Aides). Too
many kerfs will weaken a fence.
3. Keep table clean of chips and sawdust.
4. Use sharp blades, and use the right blade
for each job.
48
Carriage
Stop
5. When making miter or bevel cuts, use
extra force to hold workpiece
down because
it tends to move during these types of cuts.
6. When cutting hard woods, like oak, or
making compound
cuts, keep arm holding
saw handle rigid and pull blade through
slowly.
7. To keep cut line accurate, periodically
check blade alignment.
8. Do not cut severely warped or crooked
workpieces.
Length
Stop
Hide quick links:
Table of Contents